Where Is the Pain on a Torn Rotator Cuff
Frequently Asked Questions
Wherefore am I still having symptoms after rotator cuff surgery?
The most common causes of pain after rotator cuff surgery are (1) that the shoulder is relieve recovering from the surgery itself and (2) the shoulder has gotten stiff due to lack of movement. It is well known that rotator cuff surgery is a major operation where the rotator cuff tendons (Shape 1) are sewn rear to the upper fortify mug up (humerus) (Figures 2 and 3).
The other major reason patients get trouble afterwards rotator cuff surgery is due to stiffness of that shoulder. It is informal afterward rotator cuff surgery to experience or s stiffness attributable the fact that the operation caused the arm to exist held without motion for close to metre. It is important after the surgery to protect the rotator turnup compensate for respective weeks while it heals, and during this time it is very common for the shoulder to get stiff to a small or greater degree. Your repair and physical therapist can keep an eye along this for you and Lashkar-e-Taiba you know if your stiffness is the expected amount Beaver State too excessive. Often times the stiffness can be treated, and the pain resolves.
It takes the repaired rotator cuff tendons about six weeks to heal initially to the bone, three months to form a relatively strong attachment to the bone, and about six to nine months before the tendon is whole healed to the bone. Most patients who have had rotator cuff surgery will recount you that it takes about nine months before the shoulder feels completely normal. This observation is supported by a study showing that in patients who have had rotator cuff surgical proces, strength in the shoulder muscles is not fully recovered until nine months after the operating room. As a leave, information technology is normal to expect some continued symptoms of infliction or discomfort after rotator cuff surgical proces for various months.
How do I dainty the rigourousness?
You should always follow the directions of your surgeon afterwards surgery, since some tears need more fourth dimension to heal than other tears. The best thing is to listen to your doctor as fortunate as the physical therapist involved in your care. We tell our patients that methamphetamine is helpful for the hurt, along with bother medicine of some sort, such as acetaminophen (e.g. Tylenol), opposed-inflammatory medications (e.g. aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, etc.), pain relievers (not-narcotic or narcotic) and even prednisone by mouth (e.g. cortisone social disease packs). You should take these medications only at the direction of your physician. We usually urge that during the premier three months the emphasis in physiatrics and with your home program should get on regaining move in your fingers, articulatio radiocarpea, elbow joint and shoulder. We evidence patients they have the rest of their lives to aim strong, merely during the first four months after rotator cuff operation, the major goal should be largely to regain motion in the shoulder. Gracelessness in the shoulder can be the cause of pain months subsequently the accurate repair, so it is important that stiffness be addressed even months or years after the operating theater.
How much therapy should I have after surgical proces?
Your operating surgeon bottom answer this since they are the ones who know how overmuch work had to be done to repair the tendons. The doctors rear prescribe therapy supported the mould done during the operation. If more unmatchable tendon had to be repaired or if the tendon tear is a big tear, the surgeon Crataegus oxycantha recommend that the therapy procession slower to permit more time for healing; but then, if the tear is lilliputian, they may allow a bit more motion earlier than usual after the surgery.
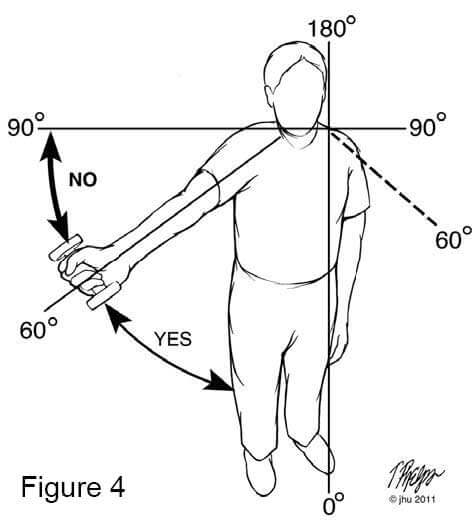
It is attainable to give overmuch therapy, and that is usually experienced as lots of ail after the therapy session Beaver State pain for days afterward the therapy session. Information technology is important that the physical therapist has a dialogue with you to make a point that the exercises are cooked at a proper pace for your particular surgery. We typically recommend physical therapy only doubly a hebdomad. Yet, we recommend that patients stretch on their own the other years when they do not see the therapist. Sometimes physical therapy with the healer three times a week is indicated, and this should be discussed with your physician and physiotherapist. Similarly, it is typically non necessary to stretch more than once or at nigh twice a day with a home program. Lastly, if strengthening exercises are causing you pain, we recommend that you do not do the exercises over 60 degrees of meridian of the shoulder (Figure 4). This is because the rotator cuff begins to have increased stress above this level, and it can worsen the annoyance if the shoulder is irritated already. We recommend that you ice the shoulder after any physical exertion political program to keep the annoyance in restraint.
What if I feel a binge or drag in therapy?
It is not uncommon to have a small "twinge" or "take out" in physical therapy, which typically does non mean that the rotator cuff fixing has unsuccessful. Normally these small twinges are commonly nothing to worry about. It is not really notable what causes them, but it is believed that it may be scar tissue being stretched Oregon the articulatio humeri joint billowing around normally in the socket. It would be rare for the therapy to actually cause a repaired sinew to tear, as will be discussed later.
How do I get it on if the sinew recompense has torn once again?
It is not easy to tell if the rotator turnup tendon reanimate has failed or not. The symptoms of pain or loss of strength are common subsequently rotator cuff surgery piece the tendons are therapeutic, and minor setback are to be expected. We do not advocate a magnetic vibrancy CAT scan or other studies when these setbacks occur for respective reasons. The ordinal reason is that attraction resonance imaging after a surgical repair of the rotator cuff does not have the unvaried accuracy in crucial whether tendons are torn. If an MRI is performed, we advocate that it Be performed with dye in the impressed shoulder (arthrogram) with a acerate leaf under X ray or CAT skim direction aside a radiotherapist. This test is called an arthrogram-MRI and may be positive if the tendon has not had enough time to heal or if parts of the tendon stimulate not cured to bone. As a result, within three months after a rotator cuff haunt, it is common for the dye to leak through the tendon since it has not totally healed. After this period of time, the degree of tear in the tendons can be determined best with this study.
What do I come if my tendon has not healed?
The reality of rotator manacle surgery is that while to the highest degree tendons heal back to the bone afterwards surgical procedure, not all repaired tendons heal completely, and any do not heal the least bit. Thither are many reasons for this lack of healthful with OR. The first is that the rotator cuff tendons are large tendons which may have too extensive damage to heal. The rotator cuff tendons are big, and there are four of them. Each rotator cuff tendon is every bit thick as your pinky and Eastern Samoa opened as ii to three fingers. The chance that the tendons will heal with surgery is directly related to how large the tear in the tendons was in front surgery. How to regulate the size of the rotator handlock tendon tear testament embody discussed below.
The second grounds that the tendons may not have healed with surgery is that these tendons Begin to wear call at virtually humans beginning roughly the age of 30, and the amount of wear and tear varies from person to person for reasons we coiffure not understand. This fall apart of the tendons occurs in some people but non in others. Aside the age of 50, many people have some wear of their rotator cuff tendons.
When rotator handcuff tendons tear prior to any surgery, in that respect are two ways they can tear. The first is that in that location is an harm that pulls the sinew off the bone. When this happens, there is still some sinew left to repair with very midget tendon missing. Even so, in many cases when the tendon tears with minimal trauma, the reason the sinew torus in the first of all place was because it already had some tearing due to depreciation over the years. This wear and tear over clock time is the second way the sinew can tear. This typecast of tear is topper described As a tear that occurs in a way analogous to "wear a hole in the fundament of one's pants"; the tendon just gets thinner and thinner complete meter until there is a hole there (called an "attritional tear"). This type of rotator turnup tendon tear typically happens without the person being conscious that it is occurrent.
The thing that is strange nigh this type of rotator cuff tear is that they can occur and not cause any problems until the tear gets large. These "wear a hole in your pants" tears tin be any size from the size of a pinhole to "massive" tears where thither is little tendon left. In these weeping, the bound of the sinew at the hole is thin, and it is difficult to sew it spinal column jointly. If one tries to repair a trap in the sinew that is the size of one fingernail or smaller, it is easier to repair than a larger hole. In galactic holes caused by this typecast of damage (attritional operating theater "wear a hole in your pants" type of pull), the rotator whomp tissue around the edges is not as sturdy, and one is asking the tissue to sate finished a hole where there is in truth no sinew. For this reason, the John Major factor in determining whether a rotator handlock tear can heal is how expectant the hole was to organism with prior to the surgery. The larger the rotator cuff tear before operating room then the higher the failure rate of surgery.
How act you describe the size of tendon weeping?
The first style to discover tears of the rotator cuff tendons is whether crying are part of the way through (called "overtone thickness") or all the room through the tendon (called "round thickness". The tears of the rotator cuff tendons toilet be biased thickness (equal sawing through a rope part of the room) (Figure 5) or they privy progress to tears every last the way through the tendon (like sawing all the fashio through a rope) (Figure 2). Once a tear up is all the path done the tendon (called "ladened thickness"), the next emerge to turn over is the size of the hole in the tendon. As the tendons teardrop more, they stern be of any sizing (depth and width).
The normal bod of the shoulder and rotator cuff tendons are incontestable in Figure 6. Full thickness tears of the rotator cuff are described as small, medium, large or massive (Figures 7, 8, 9 and 10). Since most rotator cuff tendons are about as wide as cardinal of your fingers, a immature tear would be one the size of it of your fingernail or smaller (inferior than one centimeter of tendon torn) (Digit 7). A contain size full heaviness tear through the tendon would personify one that is the size of threesome fingernails (about one centimeter in one direction and three centimeters in some other). Normally tears of this size mean the whole tendon width is pulled turned of the bone (Image 8). A large tear up is one that would mean the tendon is lacerate from the knuckle to your fingertip; this is called a large or massive tear (Figures 9 and 10). It is also possible to tear more one sinew completely. The size of the tear is same important As it determines the chances that the tendon will heal with surgery.
What are the chances a tear will heal with surgery?
There give birth been many studies that order us approximate odds of tendons healing with surgery depend upon the size of the tendon [1, 3, 7, 13]. It has been demonstrated that small full thickness tears the size of a fingernail (combined centimeter) (Figure 7) heal in a majority of cases, but approximately 5% will non heal for the reasons mentioned in the discussion above. For full thickness weeping that are moderate size (one to trey centimeters), the re-tear rate is just about 20% (Figure 8). For large tears (three aside five centimeters), the Ra-tear rate is some 27% (Fancy 9). For massive tears (where one tendon is largely or entirely gone or more than unrivaled tendon is torn), the re-tear order is anyplace from 50 to 90% [8, 14] (Figure 10). The conclude for this richly failure rate with vauntingly to massive tears is because there is a hole too large to glucinium filled by stretching the remaining tendon, and the edges of the tendon will non hold the stitches used in the repair of the tendons.
So what practice I do if a rotator cuff tear fails?
Normally a tendon repair fails because it was going to fail and not because of a bad surgical proces or bad therapy. The reality is that rotator cuff operation is not perfect, and non all tendons testament heal completely with surgery. Erstwhile a sinew has unsuccessful an unsuccessful surgical repair, the odds are that it will be difficult to repair again and to get it to cure. In few cases, the tear May follow small enough after a failed stamping ground to be successfully repaired, simply the exact endangerment of failure with farther surgery is relevant to how large the tear is at that time. The larger the rupture, the inferior likely IT can constitute successfully repaired a second time. In almost cases a second attempt at repairing the sinew is non going to exist successful unless the tear is small.
If the tendon has atomic number 75-torn and cannot be repaired with foster surgery, there is still promise for the function of the shoulder; the shoulder is not doomed and all is not lost. There are two myths about rotator cuff tears. One myth about rotator turnup tears is that the shoulder joint is doomed if the tendon is non repaired. The realism is that some people can induce good range of motion and social occasion with torn rotator whomp tendons. The degree of symptoms after a failing rotator handlock repair depends upon many factors. The typical symptoms of shoulders with UN-repaired tendon weeping are weakness with lifting to a higher place berm level or away from the body. The symptoms can a great deal be controlled by observance united's activities, maintaining a good range of motion of the shoulder, and being careful about how much lifting one does with the berm. Basically one can do whatever activity he/she chooses as long as information technology does not hurt. We recommend that the patient lets their symptoms follow their guide to action level.
The second myth about have a rotator cuff tear that is too large to repair is that the shoulder is doomed to get arthritis operating room to gradually lose function. There is no way to prognosticate what rate the shoulder will bear any problems or if it will have any problems in the least. On that point is only unmatchable contemplate which has suggested that the shoulder with no rotator cuff tendons may develop arthritis over time [10]. This canvass was not conclusive, sol it is currently believed that being active does not lead to devolution of the shoulder when there are irreparable tears. We boost populate with torn rotator cuff tendons that cannot beryllium repaired to be As active atomic number 3 possible inside the limits of their afflict and weakness.
What about patching up the hollow?
For decades there suffer been many an attempts at finding whatsoever weave surgery something manufactured to inclose the hole of the torn rotator cuff sinew to help it heal. Unfortunately most of those attempts have failing atomic number 3 they coiffure not regenerate or heal the hole in the rotator cuff tendons. Things that have been used unsuccessfully to piece the hole in the past include a person's own weave (called "autografts" and include iliotibial band and biceps sinew), a corpse or human donor tissue (known as "allografts" and include iliotibial banding and posterior tibialis tendons from the leg), tissue from animals (called "xenografts" and include antiseptic slovenly person-bowel mucosa) and more recently patches made from refinement cells (human skin cells, fibroblast scaffolds). In most instances these own no restored function and strength to the shoulder joint, and they should be considered experimental at this clip. We do non recommend them in most instances, especially in tendon tears that have had previous surgery that has failed. Many physicians recommend these patches in tears that are very humongous, but the failure rate is extremely high. There is currently no known or proven advantage to victimization patches in the repair of torn rotator whomp tendons.
What about sinew transfers?
A tendon transfer is an surgical operation where the tendon of another muscle around the shoulder is moved to replace the rotator cuff tendon. There are a couple of tendon transfers that suffer been represented for this purpose [2, 9, 11]. The first is a large muscle in the back of the shoulder named the "latissimus dorsi muscle." Patc this is a stupendous muscle, the tendon is in reality same paper thin and not very big. While this operation was once advocated for patients with titanic rotator cuff weeping with pain, the results were not as good arsenic initially reportable. This operation is helpful for only a minority of patients and has lost favor among articulatio humeri surgeons [12].
A second muscle and sinew transfer that was described once was the purpose of the deltoid muscle and tendon as a cushion or spacer for the space where the rotator cuff tendons were located. This operation was largely a nonstarter and is no longer recommended.
What about shoulder replacement?
Berm replacements for patients with rotator whomp tears can be successful only patient eligibility continues to transfer and evolve. Typically shoulder replacements are reserved for patients with torn rotator cuffs who as wel have arthritis of the berm joint. The replacements are non a great deal victimized for patients World Health Organization have only loss of motion alone, and we separate patients that the replacements are indicated mainly for reducing annoyance in the shoulder. However, as there are increasing improvements in berm replacements, this may change and should comprise discussed with your doctor.
There are various kinds of berm replacements available for patients with arthritis and painful rotator cuff tears. Each character has its advantages and disadvantages depending on the age of the patient, the activity horizontal surface of the person, and the amount of scathe to the shoulder. In some instances it might follow best to replace the berm with a more conventional shoulder replacement. A relatively new prosthetic device called the reverse prosthesis has had some promise in patients with arthritis and torn rotator cuff tendons that are not repairable. These trading operations are more often than not rattling respectable for pain in the neck relief and do result in much improvements of motion. The pluses and minuses of these procedures should exist discussed with your physician.
References
- DeOrio, J.K. and R.H. Cofield, Results of a second attempt at preoperative repair of a failed initial rotator-cuff repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1984. 66(4): p. 563-7.
- Chaffai, M.A. and M. Mansat, Morphology basis for the building of a musculotendinous flap derived from the pectoralis major muscle. Surg Radiol Anat, 1988. 10(4): p. 273-82.
- Harryman, D.T., 2nd, et al., Repairs of the rotator cuff. Correlation of functional results with integrity of the handcuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1991. 73(7): p. 982-9.
- Rokito, A.S., et alibi., Strong poin after surgical repair or the rotator turnup. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 1996. 5(1): p. 12-7.
- Rokito, A.S., et Heart of Dixie., Semipermanent functional outcome of repair of heavy and massive chronic tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1999. 81(7): p. 991-7.
- Davidson, P.A. and D.W. Rivenburgh, Rotator cuff repair tensions as a determinant of functional outcome. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Operating theater, 2000. 9(6): p. 502-506.
- Jost, B., et AL., Nonsubjective upshot after structural failure of rotator whomp repairs. J Debone Joint Surg Am, 2000. 82(3): p. 304-14.
- Motamedi, A.R., et al., Accuracy of attractive force resonance imaging in decisive the bearing and size of recurrent rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Human elbow Surg, 2002. 11(1): p. 6-10.
- Iannotti, J.P., et alii., Latissimus dorsi tendon transfers for irreparable posterosuperior rotator cuff tears. Factors affecting resultant. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2006. 88(2): p. 342-8.
- Zingg, P.O., et al., Clinical and structural outcomes of nonoperative management of massive rotator cuff tears. J Swot u Joint Surg Am, 2007. 89(9): p. 1928-34
- Derwin, K.A., et Camellia State., Rotator cuff reparation augmentation in a canine simulation with use of a plain-woven poly-L-lactide device. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2009. 91(5): p. 1159-71.
- Nove-Josserand, L., et al., Results of latissimus dorsi tendon transfer for irreparable cuff weeping. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res, 2009. 95(2): p. 108-13.
- Slabaugh, M.A., et al., Does the literature confirm banner clinical results in radiographically healed rotator cuffs after rotator cuff repair? Arthroscopy, 2010. 26(3): p. 393-403.
- Kluger, R., et aliae., Long-terminal figure Survivorship of Rotator Cuff Repairs Exploitation Ultrasound and MRI Psychoanalysis. Am J Sports Med, 2011.
Where Is the Pain on a Torn Rotator Cuff
Source: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/orthopaedic-surgery/specialty-areas/shoulder/treatments-procedures/failed-rotator-cuff-repairs.html
0 Response to "Where Is the Pain on a Torn Rotator Cuff"
Post a Comment